Dosimeter badge services for medical, dental, and veterinary businesses
Learn how Radiation Detection Company’s easy-to-use dosimetry solutions can boost the efficiency of your practice.
Radiation badges are an incredibly important piece of occupational safety for many workers. It is crucial that guidelines are followed so that badges can provide the most accurate measures of radiation and ensure personnel safety.
In this article we will take a deeper look at the steps that must be followed for the proper usage of radiation dosimeters. As always, we hope you find this article informative, and we look forward to hearing your feedback!
Radiation badges do not directly protect workers from exposure. However, they are the main component of radiation dosimetry, which documents radiation dose. This ensures that each radiation worker can monitor their exposure limits and in doing so can avoid exceeding the allowable limits established by governing bodies.
An organization's Radiation Safety Office is generally comprised of a qualified expert called a radiation safety officer (RSO), a management representative, and personnel who work with radiation-producing equipment or are otherwise at risk of occupational exposure.
This office is responsible for the implementation, coordination, and supervision of a company’s radiation safety program. It is also tasked with ensuring that the organization is following all federal, state, and local regulations. The office has the authority to enforce radiation policies and procedures with respect to both radiation safety and regulatory compliance.

As we detailed in our previous blog titled, "Radiation Safety Programs: A Comprehensive Guide," an effective radiation safety program includes:

Generally, dosimeter badges are exchanged on a monthly or quarterly basis. How frequently a badge needs to be exchanged depends on the risk of exposure in the specific workplace (higher risk means more frequent exchanges).
A control dosimeter is issued with every group of dosimetry badges sent to an organization. This control badge helps determine background radiation exposure, and captures any exposures to the shipment of badges during transit.
The control must be stored away from any radiation source to avoid picking up exposure. For more on this, please refer to our blog, "8 Must-Know Facts About Control Dosimeters."
If a badge is lost or damaged, it's crucial that this is reported to your radiation safety office immediately so the issue can be addressed, and a new badge can be ordered or given to you.
Each radiation badge will contribute to a dose report. The analysis of the badge results in the legal dose of record. Dose reports also contain a wide array of data for review by an organization's Radiation Safety Office. These reports provide detailed information needed to maintain a compliant program at the federal, state, and local levels.
Dose reports also track each worker's cumulative radiation dose throughout the year. This is important as it sheds light on how close an employee’s dose is to the annual applicable radiation dose limit as well as any ALARA notifications (as-low-as-reasonably-achievable as a worker should stay within safe dose limits.

For the purposes of external radiation exposure, “whole body” is considered to be the head, torso, arms above the elbow, or legs above the knee. These badges are generally worn on the whole body location receiving the highest radiation dose, collar, waist, or torso, with the label facing the source of the radiation.
Ring dosimeters should be worn when there is a possibility of significant exposure to the hand. It is important to wear ring dosimeters on whichever hand has the highest exposure. Sometimes meaning a ring might be worn on both hands to more accurately measure exposure. Ring dosimeters should be worn under gloves to eliminate the risk of contamination.
A wrist badge is fitted with a velcro strap which allows it to be worn around the wrist. The wrist badge is used for radiation workers whose arms may receive a higher exposure and could also be due to safety issues or dexterity problems.
Fetal Monitors are available for pregnant radiation workers to ensure the fetus does not exceed the allowable limit for the entire gestational period. These badges should be worn close to the embryo/fetus to ensure the most accurate dose is obtained.
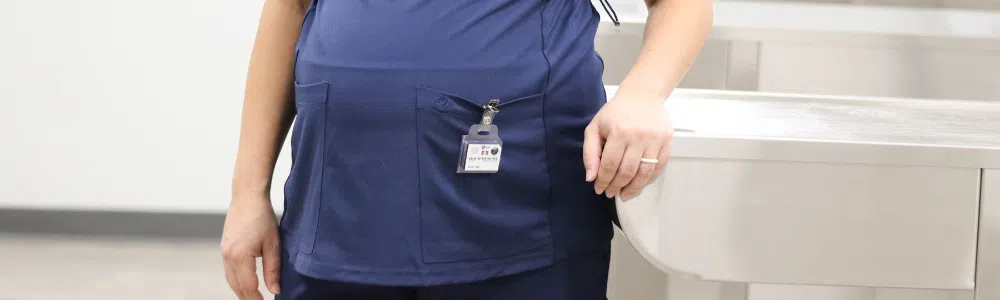
If you happen to work in an environment where the potential for some radiation exposure exists but monitoring is not required, you can request monitoring equipment.
Be sure to connect with your organization's Radiation Safety Office or officer to discuss your safety concerns, and they can assist with solutions.
Radiation Detection Company has 75 years of experience providing quality dosimetry solutions to over 28,000 companies nationwide. Not sure what type of dosimeters your organization needs? Please contact us, and our team will be happy to provide guidance.
Have a question that we did not touch on in this article? Please reach out to our Customer Care team, and one of our specialists will be more than happy to help.
Learn how Radiation Detection Company’s easy-to-use dosimetry solutions can boost the efficiency of your practice.
